The Turbocharger of a Truck: Maintenance Requirements and Fault Detection

A turbocharger is a crucial component of a truck’s engine, designed to enhance power and fuel efficiency by forcing more air into the combustion chamber. This allows the engine to burn fuel more efficiently, providing better performance and reduced emissions. However, maintaining the turbocharger is vital to ensure its reliability and to prevent costly breakdowns. Here’s what you need to know about maintaining a truck’s turbocharger and identifying signs of a faulty unit.
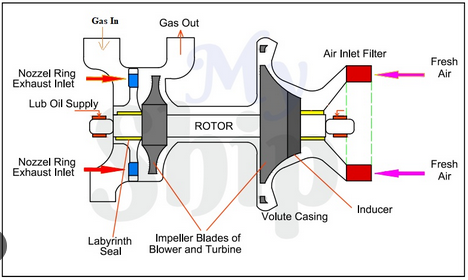
How a Turbocharger Works
A turbocharger consists of two main components: the turbine and the compressor. The turbine is driven by exhaust gases from the engine, which in turn drives the compressor. The compressor draws in air, compresses it, and sends it to the engine’s intake manifold, providing a denser air-fuel mixture for combustion. This results in increased engine power and efficiency.
Maintenance Requirements for a Turbocharger
- Regular Oil Changes:
- Turbochargers rely on engine oil for lubrication and cooling. Regular oil changes are essential to prevent oil contamination, which can damage the turbocharger.
- Use high-quality, manufacturer-recommended oil to ensure optimal performance.
2. Inspect Air Filters:
- A clean air filter prevents debris and dirt from entering the turbocharger. Replace the air filter at recommended intervals to avoid clogging and damage to the compressor.
3. Check for Oil Leaks:
- Inspect the turbocharger and surrounding areas for oil leaks, which can indicate worn seals or other issues.
4. Monitor Exhaust System:
- Ensure the exhaust system is free of blockages, as restricted exhaust flow can increase pressure on the turbocharger and reduce its efficiency.
5. Allow Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down:
- Avoid revving the engine immediately after starting or shutting it down. Allowing the engine to warm up and cool down properly protects the turbocharger from sudden temperature changes that can cause wear.
6. Periodic Inspections:
- Schedule regular inspections of the turbocharger, including checking for shaft play and examining the turbine and compressor wheels for damage.
How to Identify a Faulty Turbocharger
Recognizing the signs of a failing turbocharger can help prevent further damage to the engine. Common symptoms include:
- Loss of Power:
- A noticeable drop in engine power and acceleration may indicate that the turbocharger is not functioning correctly.
2. Excessive Exhaust Smoke:
- Blue or black smoke from the exhaust can signify oil leaks into the combustion chamber, a common issue with faulty turbochargers.
3. Unusual Noises:
- Whistling, whining, or grinding noises from the engine could indicate issues with the turbocharger’s bearings or turbine.
4. Increased Oil Consumption:
- A faulty turbocharger may lead to excessive oil consumption due to leaks or worn seals.
5. Check Engine Light:
- Modern trucks are equipped with sensors that monitor turbocharger performance. A check engine light could indicate a problem with the turbo system.
6. Boost Pressure Issues:
- A faulty turbocharger may fail to generate adequate boost pressure, leading to reduced engine performance. This can be identified through diagnostic tools.
Conclusion
The turbocharger is a vital component for enhancing a truck’s performance and fuel efficiency. Proper maintenance, including regular oil changes, air filter inspections, and periodic checks, is essential to keep the turbocharger functioning effectively. By recognizing the signs of a faulty turbocharger, truck owners and operators can address issues early and prevent costly repairs or breakdowns. Prioritizing turbocharger maintenance ensures not only the longevity of the engine but also safer and more efficient road operations.



Comments
Post a Comment